An overview of the endosymbiosis theory of eukaryote origin symbiogenesis. Endosymbiosis also explains the origin of mitochondria and chloroplast.
/2000px-Celltypes.svg-58f4417b3df78cd3fcb40917.png)
Endosymbiotic Theory How Eukaryotic Cells Evolve
The chloroplastsof red algae green algae and plants evolved from an endosymbiotic cyanobacteriumliving within a mitochondria-containing eukaryotic host cell.
Explain the theory of endosymbiosis. 10 Evidence of endosymbiotic theory. The theory of how mitochondria chloroplasts and other membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cell likely arose from a symbiosis between aerobic prokaryotes. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA which is circular not linear.
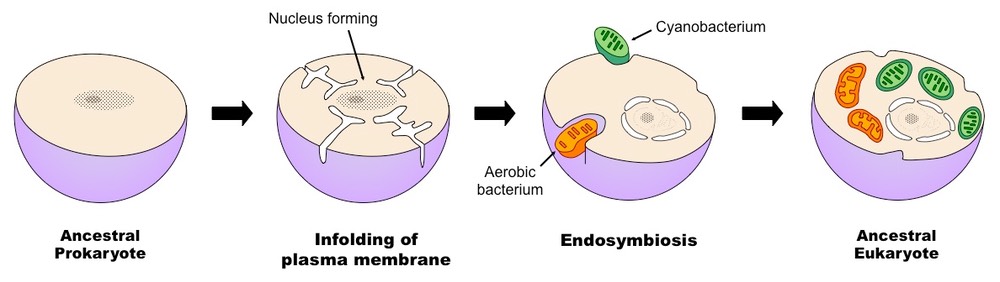
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the same size as prokaryotic cells and divide by binary fission. The prokaryotes may initially have been parasites or even an intended meal for the larger cell somehow escaping digestion. The hypothesised process by which prokaryotes gave rise to the first eukaryotic cells is known as endosymbiosis.
First proposed by Boston University biologist Lynn Margulis in the late 1960s the. Endosymbiosis is the best explanation for the evolution of the eukaryotic cell. Ribosome exists either in a larger form the 80s typical of the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
Endosymbiotic theory proposes that these organelles were once prokaryotic cells living inside larger host cells. The first step of the evolution of a eukaryotic cell is the infolding of the cellular membrane. Based on decades of accumulated evidence the scientific community supports Marguliss ideas.
The theory holds that mitochondria plastids such as chloroplasts and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. I Presence of DNA. Endosymbiosis is the process in which one organism lives within the other and the endosymbiont is the organism that lives within the other organism.
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own ribosomes which have 30S and 50S subunits not 40S and 60S. Mitochondria and Chloroplast DNA exists in closed circular form as it does in a prokaryotic cell. Ii Size of Ribosomes.
Endosymbiotic theory designates a class of hypotheses that view various organelles in eukaryotic cells as descendants of endosymbionts whereby the term endosymbiont designates a microbial cell that has come to live stably inside another microbial cell a host. In her theory of endosymbiosis Lynn Margulis emphasizes that during the history of life symbiosis has played a role not just once or twice but over and over again. Symbiogenesis or endosymbiotic theory is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms.
Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Endosymbiosis Now that we know about both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells lets look at the endosymbiosis theory. Whats more the evidence for endosymbiosis applies not only to mitochondria but to other cellular organelles as well.
The idea that chloroplasts were originally independent organisms that merged into a symbiotic relationship with other one-celled organisms dates to t. An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one. How Eukaryotic Cells Evolve Endosymbiotic Theory History.
So in accordance with the endosymbiotic theory every eukaryotic cell that we see today is actually composed of a number of other cells which were once whole in themselves. The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes. Even though the individual single-celled organisms remained separate and could survive.
Mitochondria the important energy generators of our cells evolved from free-living cells. Symbiogenesis explains the origins of eukaryotes whose cells contain two major kinds of organelle. This theory suggests that mitochondria and plastids in eukaryotic cells were once.
This process takes place when the plasma membrane folds inwards and develops an envelope around a smaller prokaryotic cell. The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory. All eukaryotic cells like your own are creatures that are made up of the parts of other creatures.
Endosymbiotic theory Also known as the theory of serial endosymbiosis SET was postulated by the American evolutionary biologist Lynn Margulis in 1967 to explain the origin of eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are believed to have evolved from early prokaryotes that were engulfed by phagocytosis. The endosymbiosis theory postulates that The mitochondriaof eukaryotesevolved from an aerobic bacterium probably related to the rickettsias living within an archaeal host cell.
The theory of how mitochondria chloroplasts and other membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cell likely arose from a symbiosis between aerobic prokaryotes and host anaerobic eukaryotic ancestors. The theory proposes that these organelles evolved from certain types of bacteria that eukaryotic cells engulfed through phagocytosis. Endosymbiosis is the theory that eukaryotic cells were formed when a prokaryotic cell ingested some aerobic bacteria.
Developed by Lynn Margulis. Iii Inhibition by.