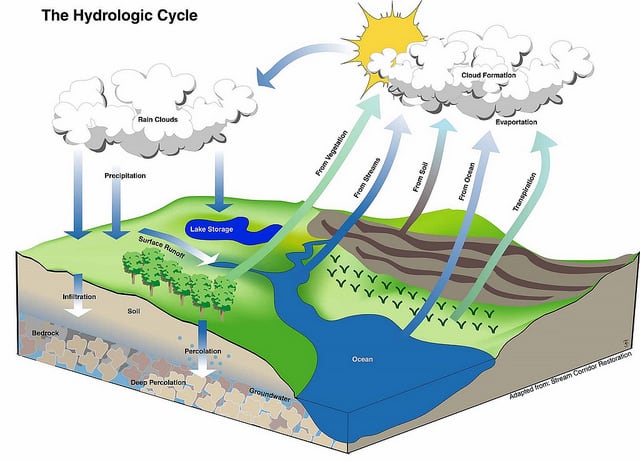
The water cycle also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle describes the continuous movement of water on above and below the surface of the Earth. Consequently the water cycle is also called the hydrologic cycle in many scientific textbooks and educational materials.
What Is The Hydrologic Cycle And Steps Of The Hydrologic Cycle Conserve Energy Future
They transmit huge quantities of water into the atmosphere via the transpiration of plants in which plants release water from their leaves during photosynthesis and from evaporation from their leaves.

Describe the hydrologic cycle. It is a cycle that replenishes ground water supplies. Evaporation Condensation Surface runoff. After reading this article you will learn about the hydrologic cycle and its components.
Lake effect snowfallis good example of the hydrologic cycle at work. Of the many processes involved in the water cycle the most important are evaporation transpiration condensation precipitation and runoff. Hydrological cycle within a drainage basin The hydrological cycle within a drainage basin is different to a global hydrological system in that it is an open system and input water transfer and.
Condensation is caused when the air cools water vapor until it reaches its saturation point. Once water reaches this point and turns into a liquid it releases all of the energy it used to get to a gaseous state. Water cycle also called hydrologic cycle cycle that involves the continuous circulation of water in the Earth-atmosphere system.
An illustrated explanation of the hydrological cycle introducing key terms. HYDROLOGIC CYCLE The hydrologic cycle is a constant movement of water above on and below the earths surface. Hydrological Cycle and Water Budgets.
Although the total amount of water within the cycle remains essentially constant its distribution among the various processes is continually changing. Water in the atmosphere in the ocean on land and underground is linked and changing one modifies the others. The water cycle also known as the hydrologic cycle defines the movement and storage of water through Earth.
Runoff a potential carrier of nutrients and sediment to streams and lakes is best described in the science of hydrology. The water cycle may also be referred to as the hydrologic cycle. It is concerned with the origin distribution and properties of water on the globe.
The hydrologic cycle also known as global water cycle or the H2O cycle describes the storage and movement of water between the biosphere atmosphere lithosphere and the hydrosphere. During this process water changes its state from one phase to another but the total number of water particles remains the same. The water cycle is the continuous process of how that water moves across the Earth and through the atmosphere connecting it all together.
The hydrologic cycle is an interactive system. Its simply transformed transported and recycled. The concept of hydrological cycle is elegantly simple.
The water cycle also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle describes the continuous movement of water on above and below the surface of the Earth. According to Wikipedia The water cycle also known as the hydrological cycle or the H2O cycle describes the continuous movement of water on above and below the surface of the Earth. Condensation is the process where the water vapor turns into a liquid and forms clouds.
The water or hydrologic cycle describes the pilgrimage of water as water molecules make their way from the Earths surface to the atmosphere and back again in some cases to below the surface. The hydrologic cycle has three main stages. Since water plays a major role in weather and climate it is important to understand the hydrologic cycle.
This gigantic system powered by energy from the Sun is a continuous exchange of moisture between the oceans the atmosphere and the land. The cycle begins as cold winds horizontal blue arrows blow across a large lake. Hydrologic cycle that contribute to the production of lake effect snow.
Environmental scientists know that the hydrologic cycle includes various processes that change water from solid to liquid to gas form and transport it to every corner of earths surface and below. The scientific discipline in the field of physical geography that deals with the water cycle is called hydrology. But its importance in the.
It begins as water vaporizes into the atmosphere from vegetation soil lakes rivers snowfields and oceans-a process called evapotranspiration. Hydrological Cycle Aquatic Environment. Menegaki in Environment and Development 2016 Hydrological cycle is also.
Role of forests in the hydrological cycle Forests play a very important role within the global and local hydrological cycles. Water can be found all around. The process is made up of six major steps and while it may change slightly from time to time it never ends or begins.
Water on Earth is constantly moving and changing states. A change in one component of the hydrologic cycle can affect weather. In terms of water the earth is a closed system so water isnt added or removed from earth.
The chloroplastsof red algae green algae and plants evolved from an endosymbiotic cyanobacteriumliving within a mitochondria-containing eukaryotic host cell. All eukaryotic cells like your own are creatures that are made up of the parts of other creatures.

From Prokaryotes To Eukaryotes
For this discussion describe the theory of endosymbiosis in your own words and identify and discuss one line the evidence for this theory.
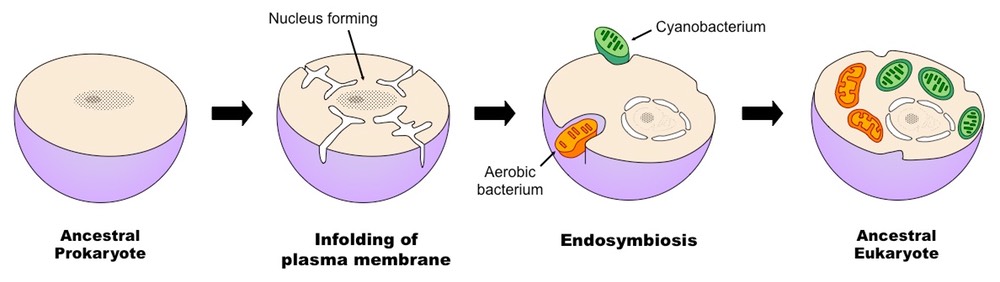
Describe the theory of endosymbiosis. Describe the endosymbiosis or endosymbiosis theory in general terms. In the Endosymbiotic theory the idea is that a eukaryotic mitochondrion evolved from an autotrophic bacterium that had been engulfed by the eukaryotic cell. This eukaryotic cell originated when an anaerobic prokaryote not able to utilize oxygen for energy lost its cell wall.
Endosymbiosis Now that we know about both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells lets look at the endosymbiosis theory. The hypothesized process by which prokaryotes gave rise to the first eukaryotic cells is known as endosymbiosis and certainly ranks among the most important evolutionary events. For full credit post unique thoughts compared to other classmate submissions on the evidence for the theory of.
So in accordance with the endosymbiotic theory every eukaryotic cell that we see today is actually composed of a number of other cells which were once whole in themselves. The bacteria travels to the intestine where it is endocytosed by an. Even though the individual single-celled organisms remained separate and could survive.
The prokaryotes may initially have been parasites or even an intended meal for the larger cell somehow escaping digestion. Mitochondria and chloroplasts divide separately from. This cell was able to arise when an anaerobic prokaryote lost its cell wall because it was unable to use oxygen for energy.
Some people refute the theory that similar DNA is due to common descent a cornerstone of endosymbiotic theory. The endosymbiont theory argues that the eukaryotic mitochodria evolved from a tiny autotrophic bacterium that was ingested by a bigger primitive heterotrophic eukaryotic cell. The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes.
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA which is circular not linear. Whats more the evidence for endosymbiosis applies not only to mitochondria but to other cellular organelles as well. Endosymbiosis is a relationship where one organism lives inside the other and both are benefited.
An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one. Endosymbiosis is the best explanation for the evolution of the eukaryotic cell. Endosymbiotic theory proposes that these organelles were once prokaryotic cells living inside larger host cells.
How Eukaryotic Cells Evolve Endosymbiotic Theory History. You can use your textbook as a reference and research this theory online as well. This theory suggests that mitochondria and plastids in eukaryotic cells were once.
A bacterial cell is ingested by a human. Mitochondria the important energy generators of our cells evolved from free-living cells. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own ribosomes which have 30S and 50S subunits not 40S and 60S.
Based on decades of accumulated evidence the scientific community supports Marguliss ideas. Genome fusion by endosymbiosis between two species one an Archaea and the other a Bacteria has been proposed as responsible for the evolution of the first eukaryotic cells. The theory of endosymbiosis Respond to the following posts The theory is that eukaryotic cells derived from interactions between various entities including spirochaetes.
Endosymbiosis is the process in which one organism lives within the other and the endosymbiont is the organism that lives within the other organism. The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory. The endosymbiosis theory postulates that The mitochondriaof eukaryotesevolved from an aerobic bacterium probably related to the rickettsias living within an archaeal host cell.
First proposed by Boston University biologist Lynn Margulis in the late 1960s the. Symbiogenesis or endosymbiotic theory is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. Symbiosis is a relationship in which organisms from two separate species live in a close dependent relationship.
Endosymbiosis endo - within is a specific type of symbiosis where one organism lives inside the other. It is thought that ancestral eukaryotic cells consumed aerobic bacteria and photosynthetic bacteria leading them to evolve into mitochondria and chloroplast respectively. Strong evidence points to endosymbiosis as the answer to the puzzle.
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the same size as prokaryotic cells and divide by binary fission.