The chloroplasts of red algae green algae and plants evolved from an endosymbiotic cyanobacterium living within a mitochondria-containing eukaryotic host cell. A bacterial cell is ingested by a human.

Endosymbiotic Theory Girlmeetsbiochemistry
This theory suggests that mitochondria and plastids in eukaryotic cells were once independent.
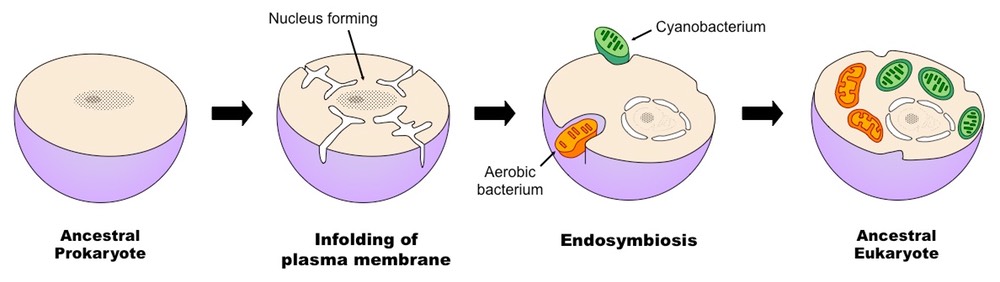
Explain the endosymbiont theory. Developed by Lynn Margulis. Ii Size of Ribosomes. The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory.
Ribosome exists either in a larger form the 80s typical of the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Symbiogenesis or endosymbiotic theory is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. Now that we know about both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells lets look at the endosymbiosis theory.
Endosymbiotic theory holds that chloroplasts and mitochondria came about through the evolution of blue-green algae and bacteria through endocytosis. First proposed by Boston University biologist Lynn Margulis in the late 1960s the. Endosymbiotic theory proposes that these organelles were once prokaryotic cells living inside larger host cells.
Though it is true that she was the first to claim the endosymbiont nature of mitochondria and chloroplasts with a handful of conclusive evidence she couldnt have done it alone. Mitochondria and chloroplasts divide separately from. I Presence of DNA.
The endosymbiotic hypothesis for the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts suggests that mitochondria are descended from specialized bacteria probably purple nonsulfur bacteria that somehow survived endocytosis by another species of prokaryote or some other cell type and became incorporated into the cytoplasm. How Eukaryotic Cells Evolve Endosymbiotic Theory History. All eukaryotic cells like your own are creatures that are made up of the parts of other creatures.
Chloroplasts produce ATP and trap photons by mechanisms that are complex and yet similar to those of certain prokaryotes. The one cell ate the other cell. They contain their own DNA and protein-synthesizing machinery similar to that of prokaryotes.
Give some evidence supporting the theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts may have arisen from prokaryotic organisms. Endosymbiotic Theory of the Origin of Eukaryotic Cells Endosymbiotic theory which is often referred to as symbiogenesis is an evolutionary theory that attempts to explain the origin of eukaryotic cells. A representation of the endosymbiotic theory An endosymbiont or endobiont is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often though not always in a mutualistic relationship.
The theory of how mitochondria chloroplasts and other membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cell likely arose from a symbiosis between aerobic prokaryotes and host anaerobic eukaryotic ancestors. Iii Inhibition by. Some people refute the theory that similar DNA is due to common descent a cornerstone of endosymbiotic theory.
The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek. The endosymbiont hypothesis Mitochondria and chloroplasts are self-dividing. These phenomena have led to the.
Mitochondria are one of the many different types of organelles in the cells of all eukaryotes. Mitochondria the important energy generators of our cells evolved from free-living cells. The endosymbiosis theory postulates that The mitochondria of eukaryotes evolved from an aerobic bacterium probably related to the rickettsias living within an archaeal host cell.
Endocytosis occurs when a substance passes into a cell through the cells membrane and then the cell plasma fuses together to keep the material inside forming an intracellular vesicle. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Even though the individual single-celled organisms remained separate and could survive.
The theory holds that mitochondria plastids such as chloroplasts and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes more closely related to bacteria than archaea taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one. The Endosymbiotic Theory Briefly describe what is meant by the endosymbiotic theory.
Mitochondria and Chloroplast DNA exists in closed circular form as it does in a prokaryotic cell. This eukaryotic cell originated when an anaerobic prokaryote not able to utilize oxygen for energy lost its cell wall. Endosymbiotic theory that attempts to explain the origins of eukaryotic cell organelles such as mitochondria in animals and fungi and chloroplasts in plants was greatly advanced by the seminal work of biologist Lynn Margulis in the 1960s.
The prokaryotes may initially have been parasites or even an intended meal for the larger cell somehow escaping digestion. 10 Evidence of endosymbiotic theory. Endosymbiotic theory can be simplified for non-scientists and science students by saying that there were two prokaryotic cells.
The endosymbiont theory argues that the eukaryotic mitochodria evolved from a tiny autotrophic bacterium that was ingested by a bigger primitive heterotrophic eukaryotic cell. The bacteria travels to the intestine where it is endocytosed by an. Many in the scientific community claim that Dr.
ἔνδον endon within σύν syn together and βίωσις biosis living. The Endosymbiotic Theory is no different. Lynn Margulis had been the first to propose the Endosymbiotic Theory.